Hironori Akiyama
About the department
In Diagnostic Imaging, we conduct X-ray imaging paying attention to justification and optimization based on the principle of ALARA (as low as reasonably achievable). Our dental radiologists prepare reports on diagnostic imaging and provide them in the hospital. A supporting radiologist (Department of Radiology, Kansai Medical University) reads images from thorough medical checkups and medical fields.
- Facility certified by academic societies
- Certified training institute of the Japanese Society for Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology
- Certified training facility for specialists of the Japanese Society for Temporomandibular Joint
Common oral diseases treated
Imaging diagnosis of maxillofacial area- Dental caries
- Periodontal disease
- Disease of root
- Cyst
- Benign tumor
- Malignant tumor
- Temporomandibular joint disorder, etc.
Director of the department

Specialty/qualification
- Board certified specialist, board certified consulting specialist and board qualified specialist of the Japanese Society for Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology
- JSOMR qualified oral radiation oncologist
(JSOMR: Japanese Society for Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology)
Chief Dental Clinician
Shinya Kotaki
Specialty/qualification
- Board Certified Specialist of the Japanese Society for Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology
- Board Qualified Specialist of the Japanese Society for Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology
Characteristics of dental care
1. Intraoral imaging
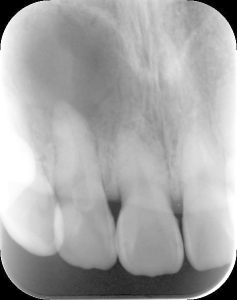
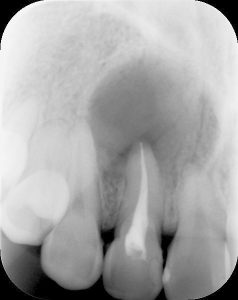
Intraoral X-ray imaging is a method in which a film or IP (imaging plate) is inserted into the oral cavity and photos are taken. This is the most commonly used imaging method in dentistry. More fine images can be obtained than panoramic X-ray imaging.
2. Panoramic X-ray imaging
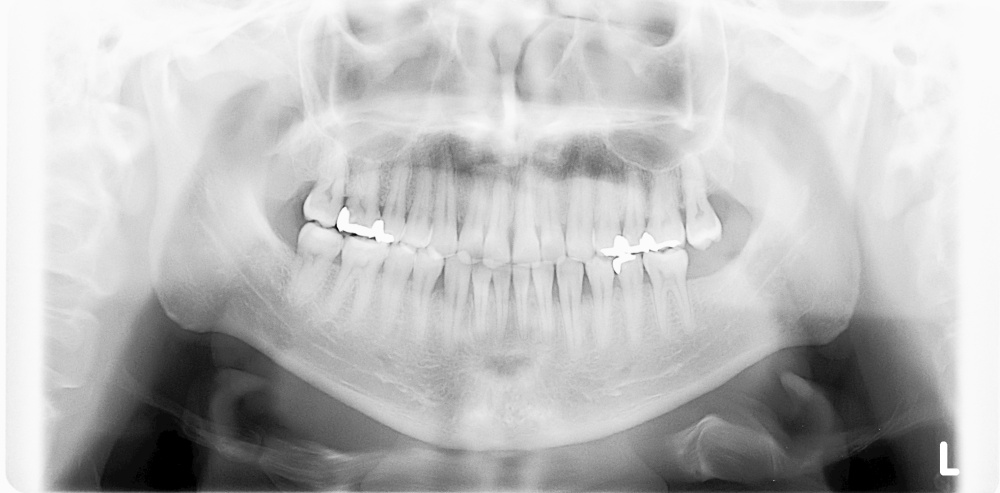
Panoramic X-ray images can visualize not only the teeth of the upper and lower jaw but also the temporomandibular joint and maxillary sinus.
Thus, it is used for screening dental caries, periodontal disease, impacted tooth, temporomandibular joint disorder, odontogenic maxillary sinusitis, cyst, benign tumor, and malignant tumor.
It takes about 15 seconds for imaging with the radiation dose equivalent to the natural radiation dose for 2 to 3 days.
3. Dental cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) imaging
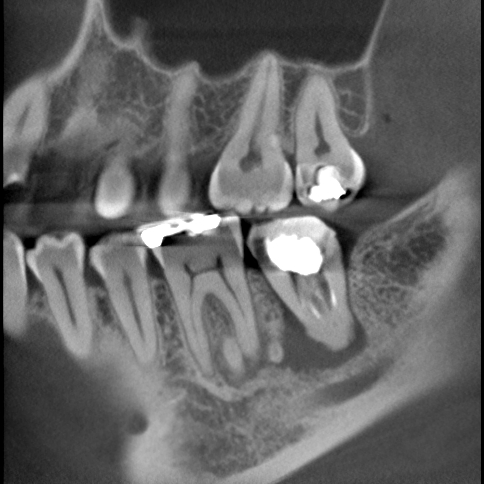
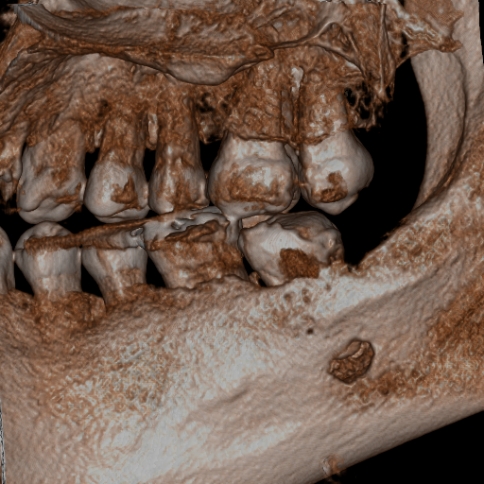
Dental CBCT imaging provides more detailed three-dimensional images of the oral cavity. In Diagnostic Imaging, we are committed to justification and optimization, consider exposure dose, and perform imaging in accordance with the guidelines for the clinical use of dental CBCT of the Japanese Society for Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology.
Efforts for state-of-the-art dental care
1. MRI of temporomandibular joint
MRI of the temporomandibular joint can be performed in about 15 minutes. We will diagnose the movement of the articular disc, the morphology of the mandibular condyle, and the morphology of the mandibular fossa by taking images of the opening and closing of the mouth.
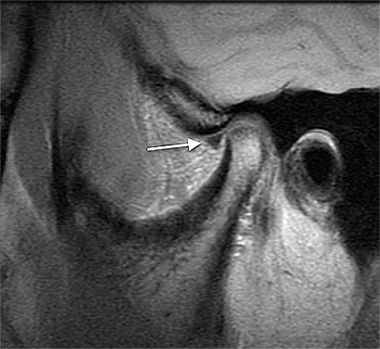
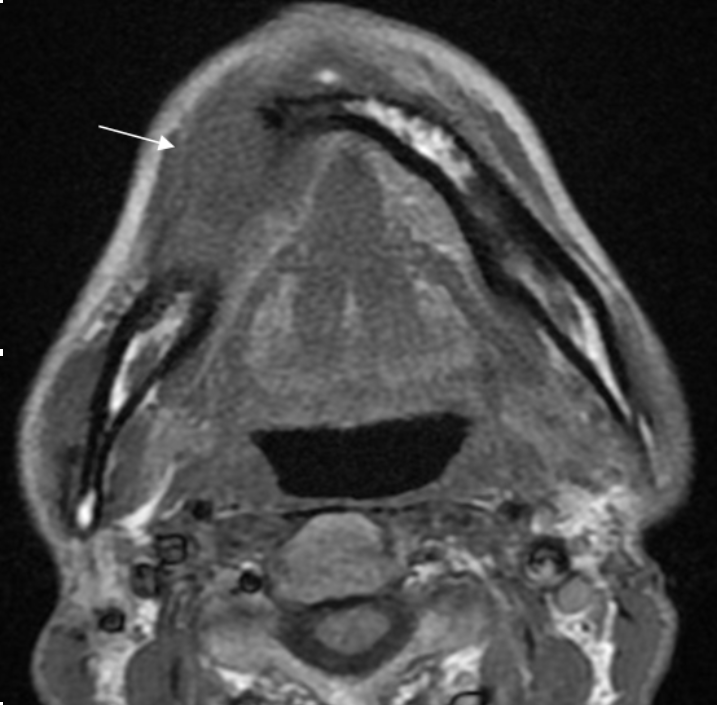
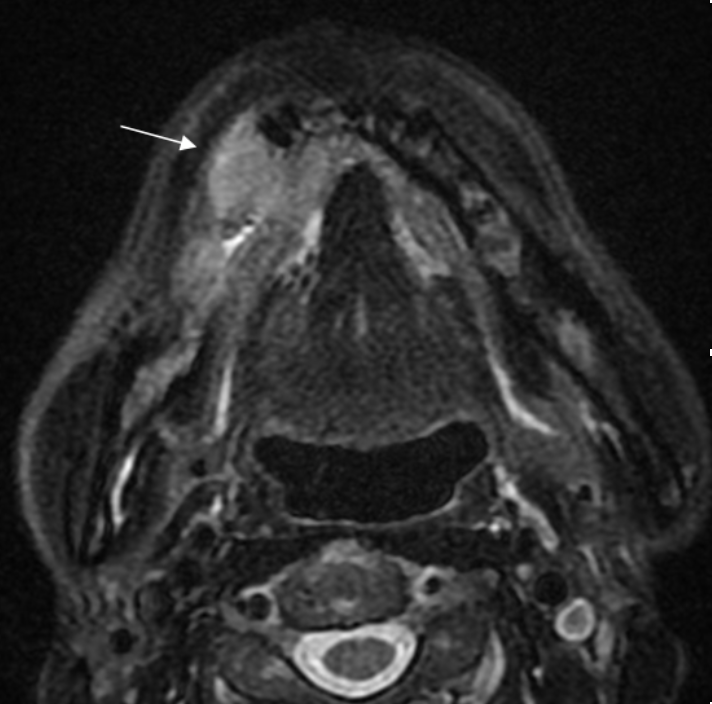
2. MRI of maxillofacial
We conduct the examination of maxillofacial area including the neck. The imaging takes about 30 minutes, and the test using a contrast agent takes about 45 minutes. We mainly examine patients with cysts, benign tumors, malignant tumors, and inflammatory diseases, etc. in the maxillofacial area.