Naohiro Iwata
About the department
At Operative Dentistry, we provide treatment for dental caries, abrasion, erosion due to acidic food and drinks, hyperesthesia, and discoloration of teeth. In addition to providing restorative treatment focusing on the preservation of a tooth and nerve (pulp) as much as possible, we emphasize preventive procedures such as professional cleaning by dental hygienists. We provide treatment aiming at achieving 8020 (eighty/twenty), keeping 20 or more teeth at the age of 80.
- Facility certified by academic societies
- Certified training facility of the Japanese Society of Conservative Dentistry(JSCD)
- Board Certified Hospital and Clinic for Training Specialists of Japan Society for
Adhesive Dentistry - Board certified training facility in laser dentistry of the Japanese Society for Laser Dentistry
- Certified MG training facility of the Japanese Academy of Sports Dentistry
Common oral diseases treated
- Dental caries
- Diseases of dental hard tissue other than dental caries
- Abrasion
- Erosion (acid erosion)
- Dysplasia
- Tooth fracture
- Hyperesthesia
- Tooth discoloration
Director of the department

Specialty/qualification
- The JSCD certified specialist of the Japanese Society of Conservative Dentistry
- Certified instructor of the Japanese Society of Conservative Dentistry(JSCD)
- Board Certified Specialist in Adhesive Dental Treatment of Japan Society for Adhesive Dentistry
- Board certified specialist in laser dentistry of the Japanese Society for Laser Dentistry
- The accredited dentist of the Japan Academy of Esthetic Dentistry
Chief Dental Clinician
Runa Sugimura
Specialty/qualification
- Authorized dentist of the Japanese Society of Conservative Dentistry(JSCD)
Characteristics of dental care
1. Restorative treatments for dental caries and dental hard tissue diseases other than dental caries
Operative dentistry treatment is comprised of a filling procedure in which a missing part of a tooth is directly repaired and an inlay repair procedure in which a tooth mold is prepared and an inlay fabricated by a dental technician is placed at the next visit. The procedure will be presented to the patient after considering the size of the disease and the patient's wish. Currently, adhesive composite resin is mainly used for a filling procedure, but a material called dental cement is used in some cases. There are three types of the inlay repair procedure depending on the material: metal, composite resin, and ceramics. Composite resin inlays and ceramic inlays are not covered by the health insurance, so they are treated at your own expense. However, they have high esthetic quality. Metal inlays are mainly covered by the health insurance.
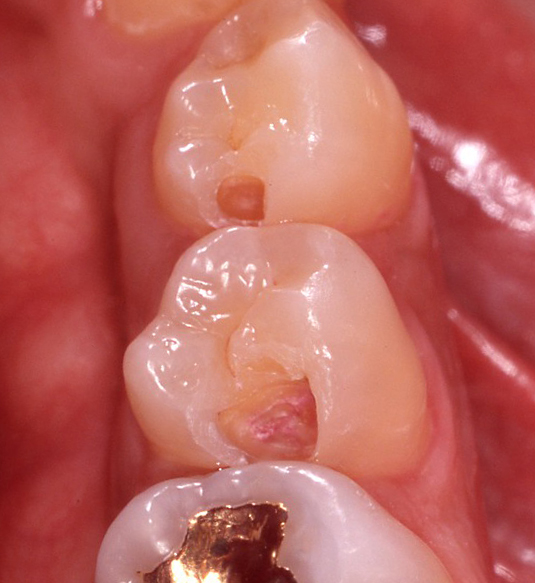
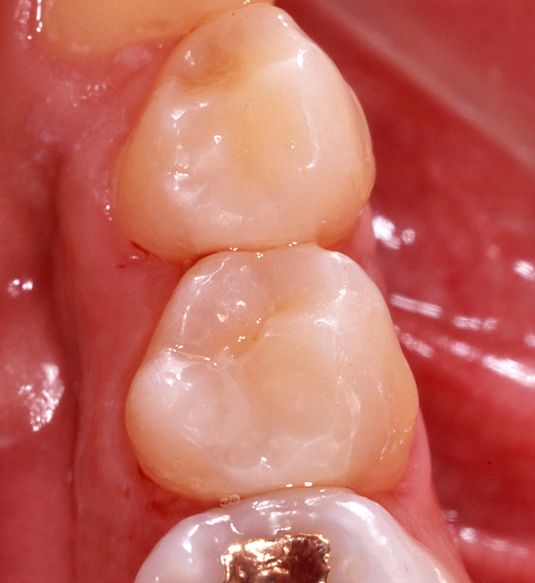
Composite resin restoration for the treatment of dental caries
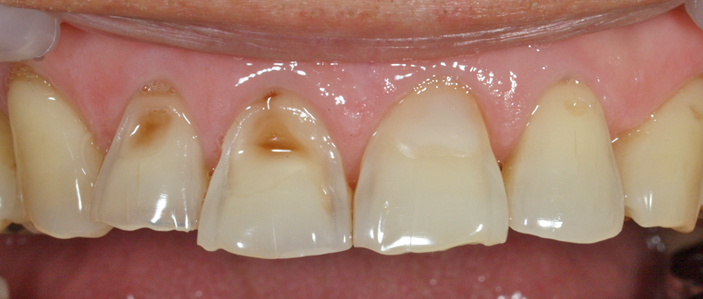
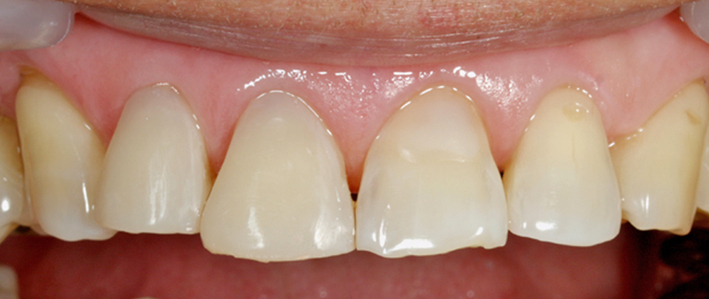
Composite resin restoration for the treatment of abrasion
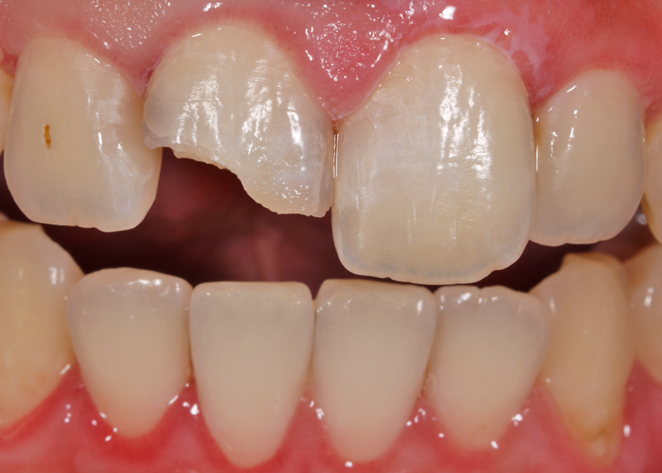
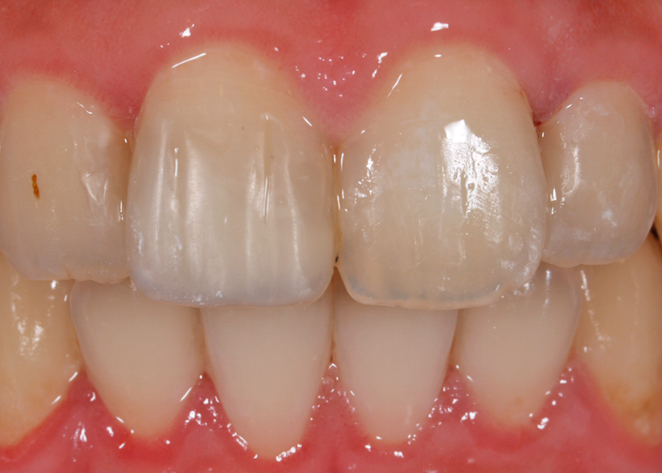
Composite resin restoration for the treatment of tooth fracture due to trauma
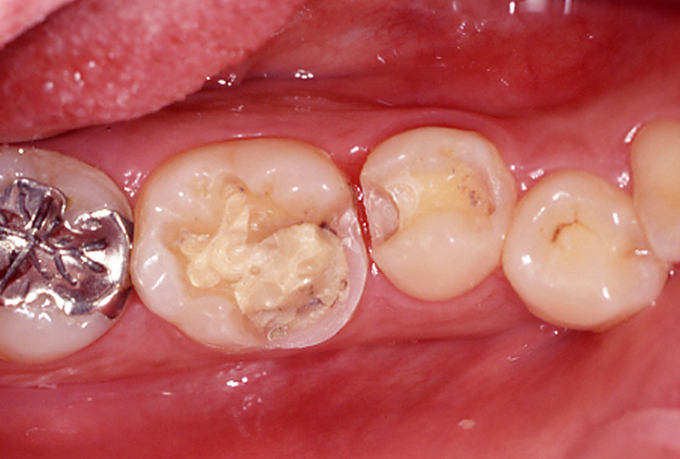
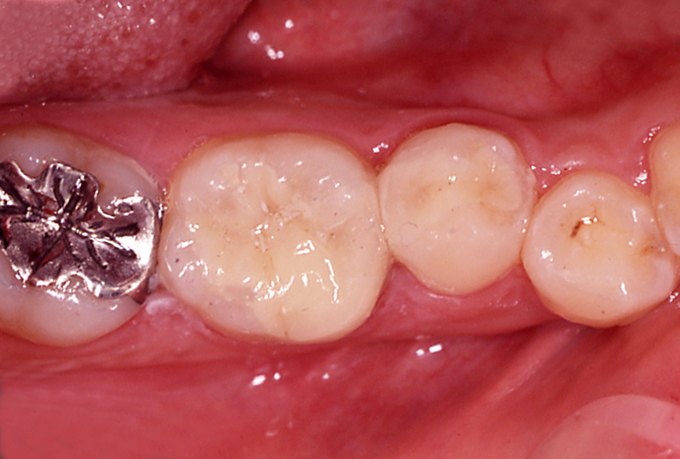
Restoration with ceramic inlay for the treatment of dental caries
2. Tooth bleaching (whitening)
The method in which color substances are decomposed by the action of bleach without grinding teeth. There are two methods: the living tooth bleaching method for teeth with nerves (pulp) and the non-living tooth bleaching method for teeth without a tooth pulp (when the pulp is dead or removed, the tooth often turns black). The living-tooth bleaching method includes an in-office whitening method performed in the clinic and a home whitening method performed by patients at home. With in-office whitening, a dentist or dental hygienist applies bleach to teeth and uses a special light to whiten the teeth. With at-home teeth whitening, patients put bleach into a dedicated tray fabricated from their impression of teeth and wear it for approximately two hours a day at home, which gradually whitens the teeth. The duration of treatment and the number of visits will differ depending on the degree of discoloration and the condition of teeth. Both whitening methods are not covered by the health insurance, so they are treated at your own expense.
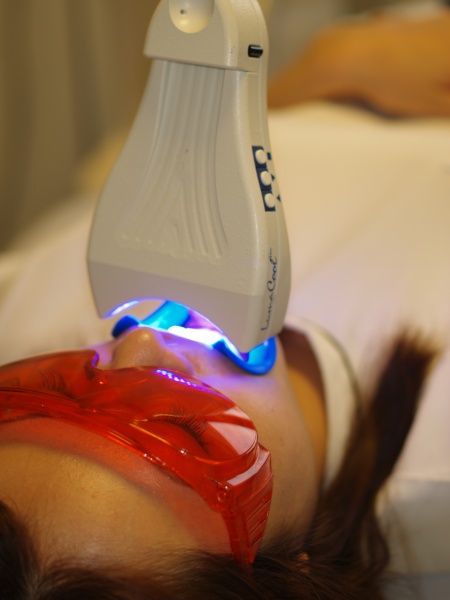
During in-office whitening
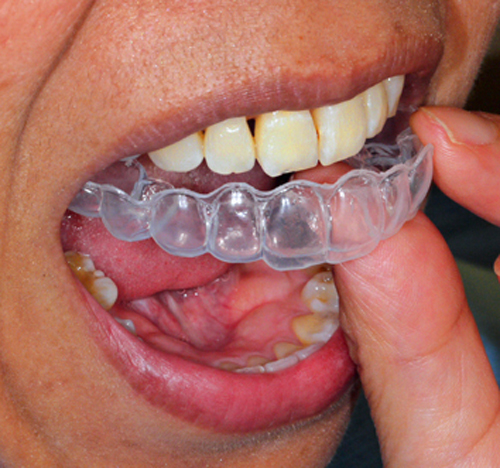
Wearing a dedicated tray for at-home whitening
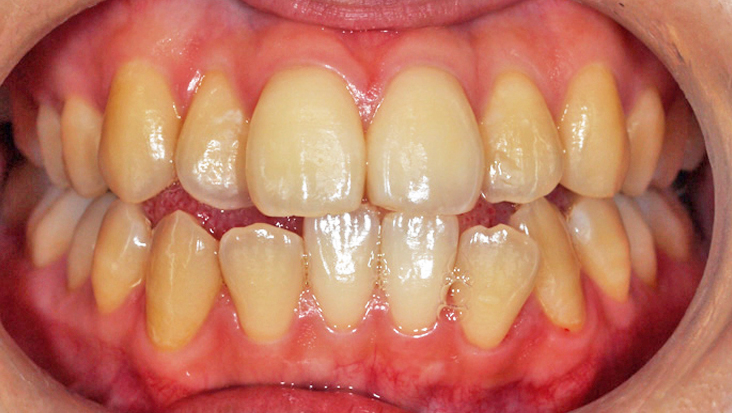
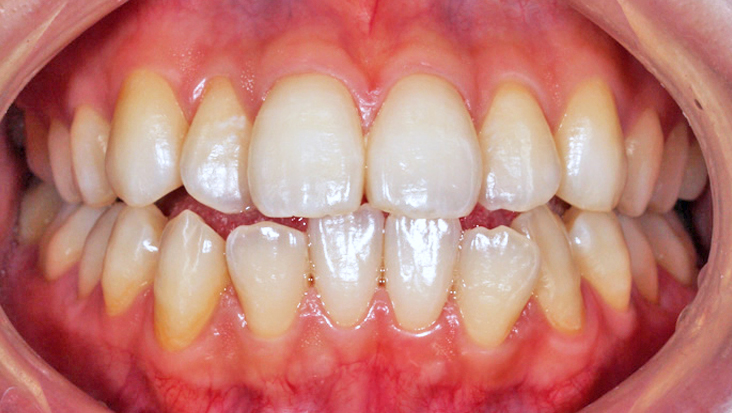
Before and after whitening
3. Professional teeth cleaning
Mainly dental hygienists perform by using a dedicated instrument, which is called Professional Mechanical Tooth Cleaning (PMTC). The thorough removal of the membrane of bacteria (biofilm) that cannot be removed by the care at home alone exerts great power for the prevention of dental caries and periodontal disease. It is also essential to restore the natural whiteness of teeth and maintain whiteness. There is a method called air flow polishing, in which a polishing agent is applied to a brush or cup and teeth are polished or fine particles are blown with compressed air to remove stains.
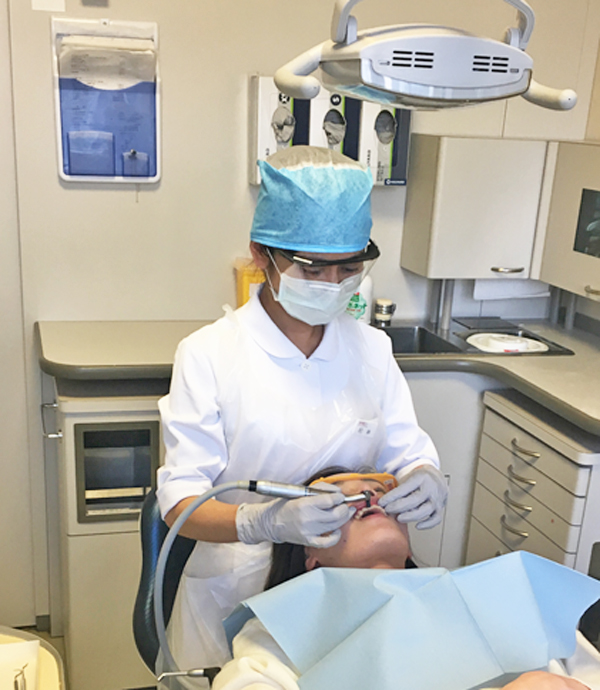
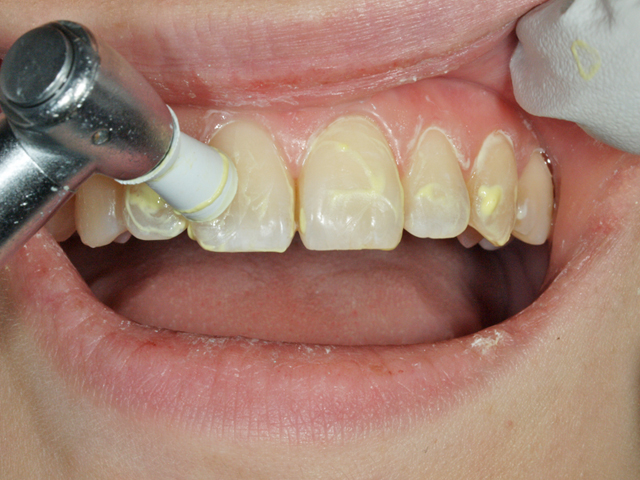
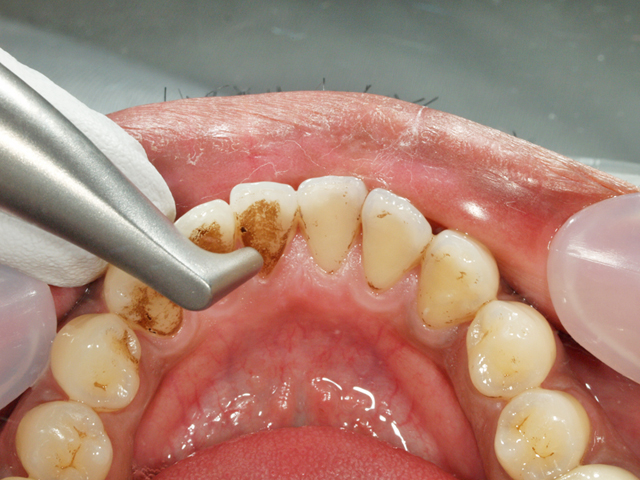
Professional Mechanical Tooth Cleaning (PMTC) by a dental hygienist
Efforts for state-of-the-art dental care
In Operative Dentistry, we perform laser treatment for dental caries, hyperesthesia, removal of melanin pigment deposition in the gingiva. There are a few types of dental lasers, which dentists choose according to cases.
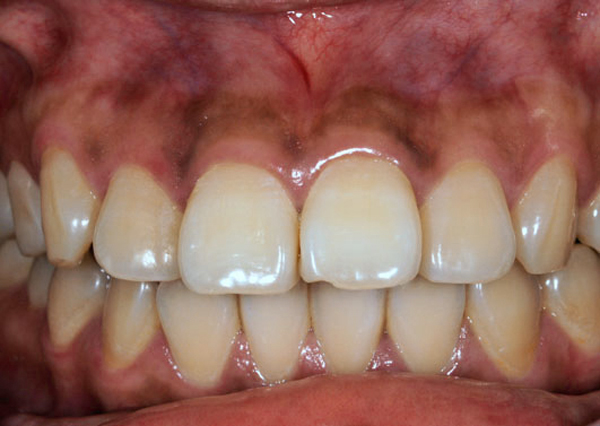
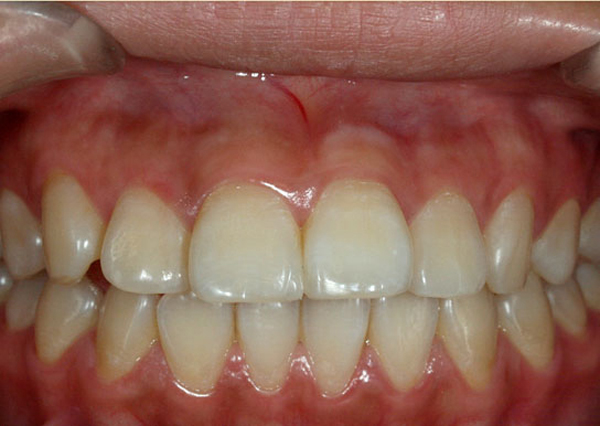
Removal of melanin pigment in the gingiva with a dental laser